Distinguishing features of kingdom prokaryotae
Distinguishing Features Of Kingdom Prokaryotae. In this online course learn about the key subjects in science. Identify the distinguishing characteristics of the Kingdom Prokaryotae. Many live in aquatic environments. The kingdom Plantae and its members plants are multicellular eukaryotic autotrophic and.
 The Classification Of Living Organisms Ppt Download From slideplayer.com
The Classification Of Living Organisms Ppt Download From slideplayer.com
Bacteria and archaea are in the Kingdom Prokaryotae or Monera Algae and protozoa are in the Kingdom Protista organisms in this kingdom are referred to as protists Fungi are in the Kingdom Fungi. The genetic material is present on a single chromosome. Some organisms have appendages such as cilia or flagella or pseudopodia to move around. Prokaryotae or Monera This kingdom was used to refer to single-celled prokaryotes such as bacteria and archaea and it rose to prominence in the 1920s because the important distinction between eukaryotes and prokaryotes was just beginning to. Organisms in the other four kingdoms all possess a nucleus 1 in their cells. They lack a nuclear membrane.
Give examples of organisms belonging to this Kingdom.
Kingdom Animalia and animals are multicellular heterotrophic motile and eukaryotic organisms. The prokaryotes are the most abundant organisms on Earth and their biomass undoubtedly outweighs all the rest of the organisms together. Biology physics and chemistry by exploring various topics related to each subject. Some organisms have appendages such as cilia or flagella or pseudopodia to move around. 2 Those without a nucleus are prokaryotes. Many live in aquatic environments.
 Source: the-kingdom-prokaryotae.subtittles12x5.online
Source: the-kingdom-prokaryotae.subtittles12x5.online
2 Those without a nucleus are prokaryotes. Some organisms have appendages such as cilia or flagella or pseudopodia to move around. The feature that most distinguishes the bacteria and blue-green algal members of the Prokaryote from the members of the other kingdoms is the lack of membrane-bound structure around the genetic material. These are the simplest forms of eukaryotes that exhibit either autotrophic or heterotrophic mode of nutrition. Although they are too small to be seen individually without powerful magnification they and the results of their activities are everywhere.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Mitochondria Golgi bodies chloroplast and lysosomes are absent. Distinguishing Features of the Five Kingdoms Plantae. The feature that most distinguishes the bacteria and blue-green algal members of the Prokaryote from the members of the other kingdoms is the lack of membrane-bound structure around the genetic material. Organisms of the kingdom Protista are thought to have existed on Earth for about a billion years. Prokaryotic cells have different characteristic features.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Prokaryotic cell size ranges from 01 to 50 μm in diameter. Organisms in the other four kingdoms all possess a nucleus 1 in their cells. This is usually the kingdom where organisms which arent animals plants or fungi go. Although they are too small to be seen individually without powerful magnification they and the results of their activities are everywhere. 2 Those without a nucleus are prokaryotes.
 Source: guidancecorner.com
Source: guidancecorner.com
The kingdoms include. Bacteria and archaea are in the Kingdom Prokaryotae or Monera Algae and protozoa are in the Kingdom Protista organisms in this kingdom are referred to as protists Fungi are in the Kingdom Fungi. Prokaryotic DNA is found in a central part of the cell called the nucleoid. Distinguishing Features of the Five Kingdoms Plantae. Kingdom Monera Monera Prokayotae moneran moneron - organisms that typically reproduce by asexual budding or fission and whose nutritional mode is absorption or photosynthesis or chemosynthesis division Archaebacteria - in some classifications considered a kingdom.
 Source: studentsace.com
Source: studentsace.com
Bacteria and archaea are in the Kingdom Prokaryotae or Monera Algae and protozoa are in the Kingdom Protista organisms in this kingdom are referred to as protists Fungi are in the Kingdom Fungi. Some examples are Diatoms Protozoans like Amoeba Paramoecium. 2 Those without a nucleus are prokaryotes. The kingdom Plantae and its members plants are multicellular eukaryotic autotrophic and. Mainly small eukaryotic organisms.
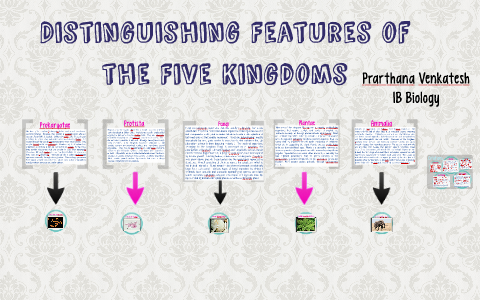 Source: prezi.com
Source: prezi.com
Without them life on Earth. The kingdom Plantae and its members plants are multicellular eukaryotic autotrophic and. Organisms of the kingdom Protista are thought to have existed on Earth for about a billion years. Such organisms are called eukaryotes. Prokaryotic cells have different characteristic features.
 Source: the-kingdom-prokaryotae.subtittles12x5.online
Source: the-kingdom-prokaryotae.subtittles12x5.online
Prokaryotic cells have different characteristic features. Some organisms have appendages such as cilia or flagella or pseudopodia to move around. General Characteristics of Prokaryotes. Correct answer - Identify the distinguishing characteristics of the Kingdom Prokaryotae. Many live in aquatic environments.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Correct answer - Identify the distinguishing characteristics of the Kingdom Prokaryotae. Prokaryotae or Monera This kingdom was used to refer to single-celled prokaryotes such as bacteria and archaea and it rose to prominence in the 1920s because the important distinction between eukaryotes and prokaryotes was just beginning to. Kingdom Animalia and animals are multicellular heterotrophic motile and eukaryotic organisms. Prokaryotic DNA is found in a central part of the cell called the nucleoid. The feature that most distinguishes the bacteria and blue-green algal members of the Prokaryote from the members of the other kingdoms is the lack of membrane-bound structure around the genetic material.
 Source: alevelbiology.co.uk
Source: alevelbiology.co.uk
Distinguishing Features of the Five Kingdoms Plantae. Prokaryotes lack an organized nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles. Prokaryotic cells have different characteristic features. Organisms of the kingdom Protista are thought to have existed on Earth for about a billion years. Prokaryotic DNA is found in a central part of the cell called the nucleoid.
 Source: digitalteachers.co.ug
Source: digitalteachers.co.ug
This is usually the kingdom where organisms which arent animals plants or fungi go. The cell wall of a prokaryote acts as an extra layer of protection helps maintain cell shape and prevents dehydration. These are the simplest forms of eukaryotes that exhibit either autotrophic or heterotrophic mode of nutrition. Bacteria and archaea are in the Kingdom Prokaryotae or Monera Algae and protozoa are in the Kingdom Protista organisms in this kingdom are referred to as protists Fungi are in the Kingdom Fungi. Organisms of the kingdom Protista are thought to have existed on Earth for about a billion years.
 Source: jid.videotronnyssa.pw
Source: jid.videotronnyssa.pw
Some organisms have appendages such as cilia or flagella or pseudopodia to move around. The kingdoms include. The genetic material is present on a single chromosome. General Characteristics of Prokaryotes. Algae slime moulds and the malaria causing Plasmodium.
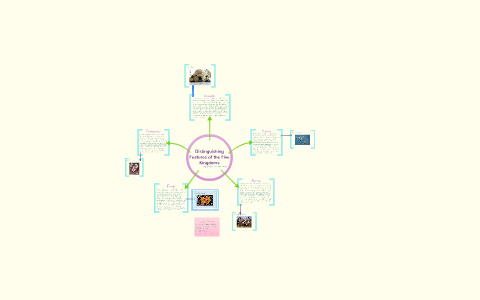 Source: prezi.com
Source: prezi.com
Prokaryotic cell size ranges from 01 to 50 μm in diameter. Organisms in the other four kingdoms all possess a nucleus 1 in their cells. Some examples are Diatoms Protozoans like Amoeba Paramoecium. Prokaryotic DNA is found in a central part of the cell called the nucleoid. Prokaryotae or Monera This kingdom was used to refer to single-celled prokaryotes such as bacteria and archaea and it rose to prominence in the 1920s because the important distinction between eukaryotes and prokaryotes was just beginning to.
 Source: the-kingdom-prokaryotae.subtittles12x5.online
Source: the-kingdom-prokaryotae.subtittles12x5.online
Kingdom Monera Monera Prokayotae moneran moneron - organisms that typically reproduce by asexual budding or fission and whose nutritional mode is absorption or photosynthesis or chemosynthesis division Archaebacteria - in some classifications considered a kingdom. Prokaryotic DNA is found in a central part of the cell called the nucleoid. 2 Those without a nucleus are prokaryotes. Without them life on Earth. Distinguishing Features of the Five Kingdoms Plantae.

Distinguishing Features of the Five Kingdoms Plantae. These are the simplest forms of eukaryotes that exhibit either autotrophic or heterotrophic mode of nutrition. The characteristics of the prokaryotic cells are mentioned below. 2 Those without a nucleus are prokaryotes. Kingdom Animalia and animals are multicellular heterotrophic motile and eukaryotic organisms.
 Source: bio.libretexts.org
Source: bio.libretexts.org
Characteristics of kingdom prokaryotae. Kingdom Monera Monera Prokayotae moneran moneron - organisms that typically reproduce by asexual budding or fission and whose nutritional mode is absorption or photosynthesis or chemosynthesis division Archaebacteria - in some classifications considered a kingdom. The feature that most distinguishes the bacteria and blue-green algal members of the Prokaryote from the members of the other kingdoms is the lack of membrane-bound structure around the genetic material. Such organisms are called eukaryotes. Organisms grouped under Kingdom Protista are all unicellular but eukaryotic organisms.
If you find this site value, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title distinguishing features of kingdom prokaryotae by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.